Section 1: What is Nutanix Database Service (NDB)?
Nutanix Database Service (NDB) is a cutting-edge database solution designed to revolutionize the way businesses manage and scale their data infrastructure. Unlike traditional databases such as SQL, Oracle, or MongoDB, NDB offers a modern, cloud-native approach that addresses the evolving needs of today’s businesses.
NDB is built on the foundation of the Nutanix platform, known for its robust infrastructure solutions. It combines the power of a distributed, hyper-converged infrastructure with advanced database management capabilities. This unique combination provides businesses with several distinct advantages:
- Simplicity: NDB simplifies database deployment, management, and scaling, allowing organizations to focus on their core business operations.
- Scalability: Businesses can scale their database infrastructure seamlessly, accommodating increasing workloads and data growth without disruptions.
- Performance: NDB offers exceptional performance and low-latency access to data, ensuring that critical applications run smoothly and efficiently.
- Cost Efficiency: By leveraging Nutanix’s infrastructure, NDB helps organizations reduce hardware and operational costs, making it a cost-effective solution.
- Security: NDB prioritizes data security, implementing robust measures to protect sensitive information.
Section 2: The Pros of Switching to NDB
When evaluating a database solution, businesses need to consider various factors that impact their operations, costs, and scalability. Nutanix Database Service (NDB) stands out as a compelling choice for numerous reasons. Let’s explore the key advantages of switching to NDB:
2.1 Cost Efficiency
NDB offers a cost-efficient approach to database management:
- Infrastructure Savings: NDB leverages Nutanix’s hyper-converged infrastructure, reducing the need for costly hardware investments. This leads to significant savings in capital expenditure.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation and management simplification in NDB result in lower operational costs. Businesses can allocate resources more effectively.
- Flexible Pricing: Nutanix often provides flexible pricing models, allowing organizations to tailor their database solution to their specific needs and budget.
2.2 Scalability
Scalability is a critical requirement for modern businesses:
- Seamless Growth: NDB enables businesses to scale their database infrastructure effortlessly. Whether it’s accommodating a sudden surge in demand or planned expansion, NDB adapts without disruptions.
- No Downtime: Businesses can add nodes and capacity to NDB without downtime, ensuring that applications continue to run smoothly even during rapid growth phases.
2.3 Performance
Performance is a top priority for database-driven applications:
- Low Latency: NDB provides low-latency access to data, making it ideal for applications that require real-time data processing, analytics, or interactive user experiences.
- Consistent Performance: Nutanix’s infrastructure ensures consistent high performance, reducing the risk of performance bottlenecks.
2.4 Simplified Management
Managing a database can be complex, but NDB simplifies the process:
- Automation: NDB incorporates automation and self-healing capabilities, reducing the burden on database administrators and minimizing human error.
- Streamlined Operations: Routine tasks like backups, updates, and failover are streamlined, allowing IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
2.5 Security
Data security is non-negotiable:
- Advanced Security Features: NDB includes advanced security features such as encryption, access controls, and auditing to safeguard sensitive data.
- Compliance: NDB helps businesses meet compliance requirements, ensuring data is handled securely and in accordance with industry regulations.
Section 3: Migrating to NDB
Migrating to Nutanix Database Service (NDB) is a crucial step for businesses looking to leverage its benefits. While the process may seem daunting, a well-planned migration can be smooth and successful. Below, I provide a step-by-step guide on how to migrate from your existing database to NDB:
3.1 Assessment and Planning
- Understand Your Current Database: Begin by thoroughly analyzing your existing database. Document its schema, data volumes, and performance characteristics.
- Define Migration Goals: Clearly define your migration goals, whether it’s cost reduction, improved performance, or enhanced scalability.
- Select Migration Tools: Choose the appropriate migration tools and software that are compatible with your current database system.
3.2 Data Migration
- Schema Migration: If necessary, modify your database schema to align with NDB’s requirements. This may involve restructuring tables or adapting data types.
- Data Extraction: Extract data from your current database using the selected migration tools. Ensure data consistency and integrity during extraction.
- Data Transformation: Transform data as needed to fit the schema of NDB. This includes data format conversions and mapping.
3.3 Migration Testing
- Set Up a Test Environment: Create a testing environment that mirrors your production environment. This allows you to validate the migration process without risking production data.
- Data Validation: Thoroughly test the migrated data to ensure accuracy and completeness. Verify that all business logic and applications work as expected with the new database.
3.4 Migration Execution
- Schedule Downtime: Plan a migration window with minimal impact on your business operations. This may involve a temporary downtime for data migration.
- Execute Migration: Perform the actual data migration, ensuring that the transformed data is transferred to NDB accurately.
3.5 Post-Migration Validation
- Data Integrity Checks: After migration, conduct extensive data integrity checks to confirm that data remains consistent and secure.
- Performance Testing: Validate that the performance of applications using NDB meets or exceeds expectations.
3.6 Monitoring and Optimization
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement monitoring tools to keep a close eye on NDB’s performance and address any issues promptly.
- Optimization: Continuously optimize your NDB deployment based on real-world usage patterns.
3.7 Training and Documentation
- Staff Training: Train your IT and database administration teams on managing NDB effectively.
- Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation on your NDB deployment, including configurations, best practices, and troubleshooting procedures.
Section 4: Real-World Use Cases
The true measure of any database solution’s effectiveness lies in its real-world applications. Nutanix Database Service (NDB) has empowered numerous businesses across various industries to achieve their database management goals. Let’s explore some compelling real-world use cases:
4.1 E-commerce Powerhouse
Case Study: A leading e-commerce giant
This e-commerce giant faced immense challenges handling the ever-increasing volume of customer data and transaction records. They needed a solution that could scale seamlessly to meet peak shopping seasons and provide a reliable, low-latency experience for their customers.
Nutanix Database Service came to the rescue:
- Scalability: NDB’s ability to scale on-demand ensured that the platform effortlessly handled peak loads without performance degradation.
- Cost Efficiency: The e-commerce company reported significant cost savings due to reduced hardware and operational expenses.
- Real-time Analytics: NDB’s low-latency access enabled the company to perform real-time analytics, leading to data-driven insights for marketing and inventory management.
4.2 Healthcare Transformation
Case Study: A major healthcare provider
This healthcare organization was dealing with sensitive patient records and needed a secure, high-performance database solution to support critical applications like Electronic Health Records (EHR) and telemedicine.
Nutanix Database Service delivered:
- Security: NDB’s advanced security features ensured HIPAA compliance and safeguarded patient data.
- Performance: The healthcare provider experienced a dramatic improvement in application response times, enhancing patient care.
- Disaster Recovery: NDB’s built-in disaster recovery capabilities ensured data availability during emergencies.
4.3 Tech Startup Success
Case Study: A fast-growing tech startup
A tech startup was rapidly expanding and needed a database solution that could grow with them. They sought a cost-effective yet high-performance option.
Nutanix Database Service provided:
- Scalability: NDB seamlessly accommodated the startup’s growth without disruptions, eliminating the need for frequent migrations.
- Cost Savings: The startup reported substantial cost savings compared to their previous database solution.
- Focus on Innovation: With NDB handling database management, the startup’s IT team could focus on innovation and product development.
These real-world use cases demonstrate the versatility and impact of Nutanix Database Service across different industries. Whether it’s e-commerce, healthcare, or startups, NDB has proven to be a game-changer for businesses seeking a modern, efficient, and scalable database solution.
Section 5: Architecture and Design
Understanding the architecture and design of Nutanix Database Service (NDB) is essential for businesses considering its adoption. NDB’s robust architecture is at the heart of its performance, scalability, and reliability. Below, I dive into the core components and design principles of NDB:
5.1 Distributed Architecture
NDB leverages a distributed architecture that distributes data and workload across multiple nodes. This approach offers several benefits:
- High Availability: Data redundancy and distribution ensure high availability and fault tolerance.
- Scalability: New nodes can be added seamlessly to accommodate growing data and workloads.
- Performance: Data access is optimized through parallel processing.
5.2 Data Tiering
NDB incorporates a data tiering strategy that categorizes data based on its access frequency:
- Hot Data: Frequently accessed data is stored on high-performance storage tiers, ensuring low-latency access.
- Warm Data: Data that is less frequently accessed is moved to cost-effective storage tiers, optimizing resource utilization.
5.3 Automation and Self-Healing
NDB includes automation and self-healing mechanisms:
- Auto-scaling: NDB automatically scales resources up or down based on workload demand.
- Data Replication: Data is replicated for redundancy and disaster recovery, with automated failover mechanisms.
5.4 Native Services Integration
NDB seamlessly integrates with other Nutanix native services:
- Prism Management: Administrators can manage NDB through the Prism management interface, simplifying overall infrastructure management.
- Era: Nutanix Era provides database management automation, further simplifying database operations.
5.5 Security Layers
NDB’s architecture includes multiple security layers:
- Encryption: Data is encrypted at rest and in transit to protect against unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Role-based access controls ensure that only authorized personnel can manage and access the database.
5.6 Customization and Extensibility
NDB’s architecture allows for customization and extensibility:
- Application Integration: NDB can be integrated seamlessly with a wide range of applications through standard APIs.
- Custom Modules: Businesses can develop custom modules or extensions to tailor NDB to their specific needs.
5.7 High-Level Diagram
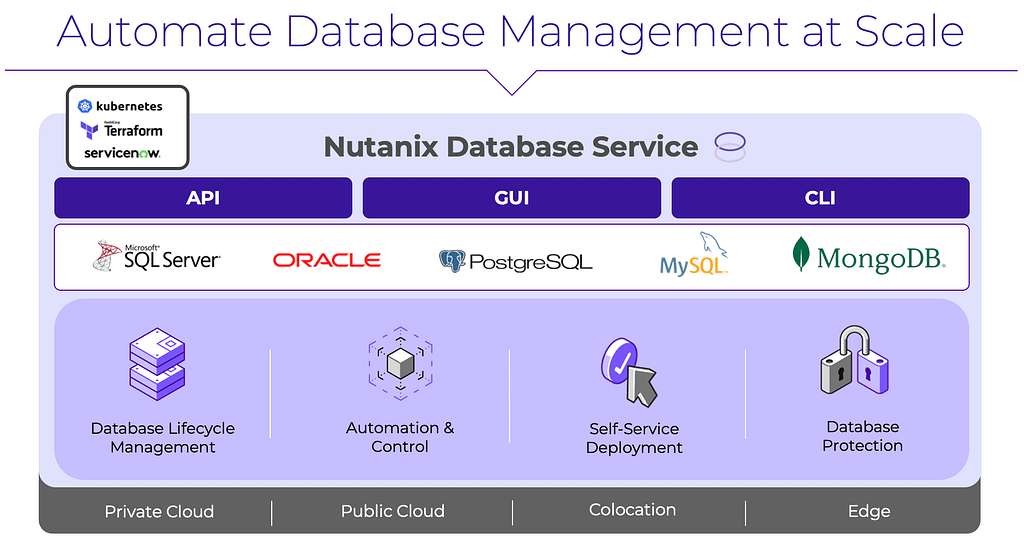
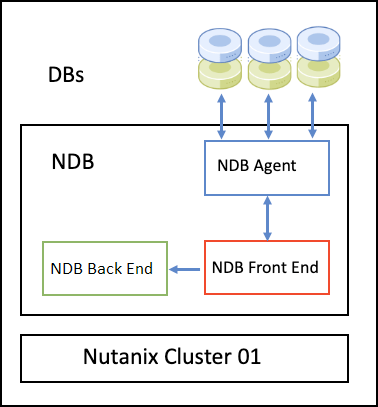
The high-level architecture diagram provides an overview of how data flows through NDB’s distributed infrastructure, highlighting key components and their interactions.
Section 6: Conclusion and Additional Resources
6.1 Conclusion
In my exploration of Nutanix Database Service (NDB), I’ve uncovered a modern, cloud-native database solution that offers businesses a compelling alternative to traditional databases. NDB’s architecture, scalability, cost-efficiency, and security features make it a standout choice for organizations seeking to optimize their database management.
By switching to NDB, businesses can:
- Achieve cost savings through infrastructure optimization.
- Scale effortlessly to accommodate data growth and changing workloads.
- Experience superior performance with low-latency data access.
- Simplify database management through automation.
- Strengthen data security and meet compliance requirements.
As technology evolves and data becomes increasingly critical, NDB empowers businesses to stay competitive and agile.
6.2 Additional Resources
For those eager to delve deeper into Nutanix Database Service (NDB), here are some valuable resources:
- Nutanix NDB Official Website: Explore Nutanix’s official website for comprehensive information, documentation, and product details about NDB.
- Nutanix Documentation: Access Nutanix’s documentation hub for in-depth guides, best practices, and technical information on NDB.
- Database Workloads on Nutanix: Article focused on the components required to run databases on Nutanix
- Nutanix Blog: Stay updated with the latest blog posts on NDB, featuring use cases, success stories, and industry insights.
- Nutanix on Twitter: Follow Nutanix on Twitter for real-time updates, news, and announcements related to NDB and other products.
In conclusion, Nutanix Database Service (NDB) offers a transformative solution for businesses seeking to optimize their database infrastructure, harness the power of automation, and scale with confidence. I encourage you to explore the resources provided above to embark on your NDB journey.